How Does Pill Counting Machine Work?
2025-11-04 11:13:43
Pill counting machines have revolutionized pharmaceutical packaging by automating the tedious process of manually counting tablets and capsules. These sophisticated devices combine advanced sensor technology with precision engineering to deliver accurate, high-speed counting for various pharmaceutical applications. Understanding how Pill Counting Devices operate is essential for manufacturers seeking to optimize their production lines, reduce labor costs, and maintain consistent quality standards. Modern Electronic Pill Counters utilize multiple detection methods including photoelectric sensors, vibration channels, and computerized control systems to ensure each bottle contains the exact number of tablets specified, achieving accuracy rates exceeding 99.8% while processing between 10 to 40 bottles per minute.
Core Operating Principles of Pill Counting Technology
Sensor-Based Detection Systems
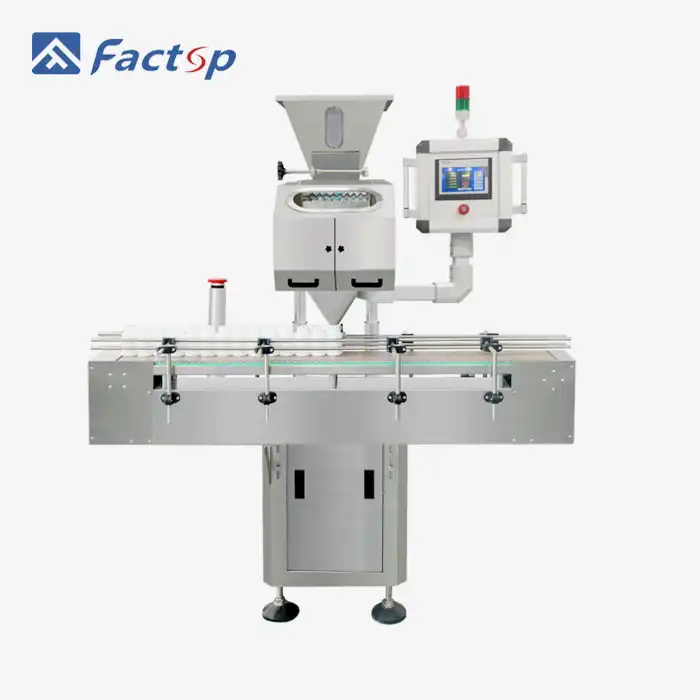
The foundation of any Electronic Pill Counter lies in its sensor technology, which serves as the machine's eyes. Pill Counting Devices typically employ photoelectric sensors positioned strategically along the counting channel. When tablets or capsules pass through a narrow counting channel, they interrupt an infrared beam, triggering the sensor to register each unit. The SL-8 model from Factop utilizes advanced optical sensors capable of detecting pills ranging from #00 to #5 capsules and tablets measuring 3-22mm in diameter. These sensors operate at high frequencies, allowing rapid detection without compromising accuracy. The sensor system connects to a microprocessor that processes the signals in real-time, maintaining a running count throughout the filling operation. Modern Pill Counting Devices incorporate dual-sensor configurations to eliminate counting errors caused by pills touching or overlapping during passage. This redundancy ensures that even at maximum speeds of 40 bottles per minute, the accuracy remains above 99.8%, meeting stringent pharmaceutical standards for packaging integrity.
Vibratory Feeding Mechanisms
The vibratory feeding system represents another critical component in how Pill Counting Devices function effectively. Before pills reach the counting sensors, they must be singulated—separated into individual units flowing in a controlled stream. This is achieved through precision-engineered vibrating channels that gently agitate tablets, causing them to align and move forward in single file. The Electronic Pill Counter adjusts vibration intensity based on the size, shape, and weight of the product being counted. For lightweight capsules, gentler vibration prevents damage, while denser tablets may require stronger agitation for optimal flow. The SL-8 model's vibratory system accommodates various bottle sizes from 10ml to 500ml and adapts to both round and square bottle configurations. The feeding rate synchronizes with the counting speed to prevent bottlenecks or gaps in the stream, ensuring continuous operation. This mechanical precision, combined with adjustable amplitude controls, allows operators to fine-tune performance for different products without requiring extensive recalibration between production runs.
Computerized Control and User Interface
Modern Pill Counting Devices integrate sophisticated computerized control systems that transform raw sensor data into actionable counting information. The Electronic Pill Counter features a user-friendly touchscreen interface where operators input the desired count (ranging from 1 to 9,999 pills per bottle), select product parameters, and monitor real-time production statistics. The microprocessor continuously calculates the fill rate, adjusts the stop-gate timing to halt product flow at precisely the correct count, and logs production data for quality assurance purposes. Advanced models incorporate programmable logic controllers (PLCs) that can store multiple product recipes, enabling quick changeovers between different tablet types or bottle sizes. The control system also monitors machine performance, alerting operators to potential issues such as sensor malfunctions, low product levels in the hopper, or deviations from expected counting accuracy. This intelligence layer transforms the Electronic Pill Counter from a simple mechanical device into an integrated production asset capable of self-monitoring and optimization, significantly reducing the need for constant human supervision while maintaining pharmaceutical-grade quality standards.
Mechanical Workflow and Process Integration
Product Loading and Hopper Design
The counting process begins long before pills reach the sensors, starting with how Pill Counting Devices receive and manage bulk product. The hopper design plays a crucial role in maintaining consistent feed rates and preventing product degradation. Factop's Electronic Pill Counter features a generously sized hopper constructed from pharmaceutical-grade stainless steel that resists corrosion and facilitates easy cleaning between production runs. The hopper's interior surfaces incorporate gentle slopes and rounded corners to prevent pills from becoming trapped or crushed. A level sensor within the hopper alerts operators when product supplies run low, preventing counting interruptions that could disrupt production schedules. For moisture-sensitive products like effervescent tablets, the hopper design includes optional sealed covers that maintain environmental control. The transition from hopper to vibratory channel represents a critical engineering challenge—the opening must be large enough to prevent jamming yet restrictive enough to control flow. Pill Counting Devices address this through adjustable gate mechanisms that operators can configure based on product characteristics, ensuring smooth transitions from bulk storage to the precision counting phase without causing mechanical stress or product damage.
Bottle Positioning and Fill Sequence
Precise bottle positioning is essential for Electronic Pill Counter operation, ensuring pills discharge directly into containers without spillage or contamination. The SL-8 model incorporates an automated bottle indexing system that accepts containers ranging from 10ml to 500ml in both round and square configurations. Bottles advance along a conveyor system equipped with mechanical guides that center each container beneath the discharge chute. Photoelectric sensors detect bottle presence and communicate with the control system, which initiates the counting sequence only when a container is properly positioned. During filling, the discharge gate opens, allowing the pre-counted quantity of pills to fall into the bottle. The gate then closes immediately, and the filled bottle advances while an empty container moves into position. This synchronized dance between Pill Counting Devices, bottle handling equipment, and control systems occurs repeatedly throughout production shifts, with the SL-8 capable of completing 10 to 40 fill cycles per minute depending on the count quantity and product characteristics. The mechanical precision required to maintain this rhythm while preserving accuracy demonstrates the sophisticated engineering that transforms bulk tablets into precisely counted, retail-ready packages.
Quality Control and Verification Systems
Quality assurance represents a critical function within modern Pill Counting Devices, ensuring every bottle meets exact specifications before leaving the production line. Electronic Pill Counters incorporate multiple verification mechanisms throughout the counting process. Primary verification occurs through the sensor system's inherent accuracy—the SL-8 model achieves greater than 99.8% precision through its dual-sensor configuration. Secondary verification involves statistical sampling, where the control system flags bottles for manual recount at predetermined intervals, providing ongoing validation of machine performance. Advanced models include weight-check systems that weigh filled bottles against expected weights calculated from individual pill mass and count quantity. Discrepancies trigger automatic rejection, diverting non-conforming bottles from the production line. Factop's quality philosophy extends beyond the counting mechanism itself—each Electronic Pill Counter undergoes rigorous factory testing before shipment, including extended runtime validation with various product types. This comprehensive approach to quality control, from machine manufacturing through operational deployment, ensures Pill Counting Devices consistently deliver the pharmaceutical-grade accuracy required for regulatory compliance and patient safety in medication packaging applications.
Technical Specifications and Performance Capabilities
Speed, Accuracy, and Capacity Parameters
Understanding the performance envelope of Pill Counting Devices helps manufacturers select appropriate equipment for their production requirements. The Factop SL-8 Electronic Pill Counter exemplifies modern capability, processing 10 to 40 bottles per minute with accuracy exceeding 99.8%. This speed range accommodates various operational scenarios—lower speeds for high-count bottles (approaching the 9,999-pill maximum) or delicate products requiring gentle handling, and maximum speeds for standard prescription counts of 30, 60, or 90 pills per bottle. The machine's versatility extends to product compatibility, handling capsules from #00 to #5 sizes, softgel capsules, and tablets ranging from 3mm to 22mm in diameter. This broad range encompasses virtually all pharmaceutical tablet configurations, from tiny nitroglycerin pills to large calcium supplements. Power requirements remain modest at 220/380V/50Hz, allowing integration into standard pharmaceutical facility electrical infrastructure. The compressed air requirement of 0.6MPa supports pneumatic actuators that control gates and positioning mechanisms. Physical dimensions of 1360×1650×1650mm and weight of 350kg indicate substantial construction using industrial-grade materials, yet the footprint remains compact enough for integration into existing packaging lines without requiring extensive facility modifications.
Material Construction and Sanitation Features
Pharmaceutical manufacturing demands equipment constructed from materials that resist corrosion, facilitate thorough cleaning, and prevent product contamination. Pill Counting Devices used in pharmaceutical applications typically feature contact surfaces made from 316L stainless steel, which offers superior resistance to the acidic cleaning agents and sanitizing solutions used in GMP facilities. The SL-8 Electronic Pill Counter incorporates smooth, crevice-free surface finishes that prevent pill fragments or dust accumulation in hard-to-clean areas. All product-contact components disassemble without tools, allowing rapid changeover and thorough sanitization between different products or production campaigns. This design philosophy aligns with current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) requirements that mandate prevention of cross-contamination between different pharmaceutical products. Non-contact surfaces utilize industrial-grade materials selected for durability and chemical resistance, ensuring long service life even in demanding production environments. The electrical components receive appropriate ingress protection ratings, shielding sensitive electronics from dust and moisture common in pharmaceutical packaging areas. These material choices and design considerations transform Pill Counting Devices from simple counting machines into validated pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment capable of meeting regulatory scrutiny and delivering reliable performance over years of continuous operation.
Integration with Pharmaceutical Production Lines
Modern Electronic Pill Counters function not as standalone machines but as integrated components within comprehensive pharmaceutical packaging systems. The SL-8 model features industry-standard interfaces that enable communication with upstream equipment (bottle unscramblers, container cleaners) and downstream machinery (capping systems, labeling equipment, cartoning machines). This integration capability allows manufacturers to create fully automated packaging lines where bottles flow continuously from empty containers to finished, labeled products without manual intervention. The control system outputs production data in formats compatible with Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) platforms, providing real-time visibility into production metrics, downtime events, and quality statistics. Pill Counting Devices can receive production instructions digitally, automatically adjusting count quantities and product parameters based on production schedules without requiring operator input for each changeover. This connectivity transforms the Electronic Pill Counter into a smart manufacturing node, contributing data to broader facility analytics while responding to production demands dynamically. For manufacturers pursuing Industry 4.0 initiatives, modern Pill Counting Devices provide essential building blocks for creating intelligent, data-driven pharmaceutical packaging operations that optimize efficiency while maintaining rigorous quality standards.
Maintenance, Troubleshooting, and Operational Best Practices
Preventive Maintenance Protocols
Sustained performance of Pill Counting Devices requires systematic preventive maintenance that addresses mechanical wear, sensor calibration, and cleanliness standards. Daily maintenance procedures for the Electronic Pill Counter include visual inspection of product-contact surfaces for residue buildup, verification that sensors are clean and unobstructed, and confirmation that vibratory channels operate smoothly without unusual noise or vibration patterns. Weekly maintenance extends to lubrication of moving parts using pharmaceutical-grade lubricants that won't contaminate products if minor leakage occurs. Monthly procedures involve sensor calibration verification using standardized test tablets of known dimensions, ensuring counting accuracy remains within specification. The compressed air system requires regular attention—inline filters need replacement according to manufacturer schedules to prevent contaminated air from affecting pneumatic actuators. Factop provides comprehensive maintenance documentation with each Electronic Pill Counter, detailing inspection intervals, recommended spare parts inventories, and step-by-step procedures for common service tasks. This structured approach to maintenance maximizes uptime, extends equipment service life, and prevents minor issues from escalating into production-disrupting failures. Facilities that implement disciplined preventive maintenance programs consistently achieve higher Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) scores and lower total cost of ownership for their Pill Counting Devices.
Common Operational Challenges and Solutions
Even well-maintained Pill Counting Devices occasionally encounter operational challenges that require troubleshooting expertise. Counting inaccuracies represent the most common concern, typically resulting from contaminated sensors, improper vibration settings, or pills that don't conform to specification (irregular shapes, excessive coating variations). The Electronic Pill Counter's diagnostic system assists operators by displaying real-time sensor status and historical accuracy trends that help identify when issues began. For products that consistently generate counting errors, adjusting vibratory amplitude or modifying sensor sensitivity often resolves the problem without requiring service intervention. Jamming in the counting channel typically indicates either improper product characteristics or mechanical issues with the vibratory system. Clearing jams requires stopping production, removing affected product, inspecting for damaged pills that might indicate upstream manufacturing problems, and adjusting operating parameters before resuming. Bottle positioning errors usually trace to worn guide rails or photoeye sensors that need cleaning or replacement. Factop's technical support team provides remote diagnostics for complex issues, accessing machine data through secure connections to analyze performance patterns and recommend corrective actions. This combination of operator-level troubleshooting capability and expert technical support ensures Pill Counting Devices maintain high availability even when operational challenges arise.
Operator Training and Skill Development
Maximizing the performance potential of Pill Counting Devices depends fundamentally on operator knowledge and skill development. Comprehensive training programs address machine operation, routine maintenance, basic troubleshooting, and quality verification procedures. Initial training for the SL-8 Electronic Pill Counter typically spans two to three days, combining classroom instruction on operating principles with hands-on practice in setup, operation, and changeover procedures. Operators learn to interpret the control system's displays, recognize normal versus abnormal operating sounds and vibrations, and execute standard cleaning protocols. Advanced training modules cover parameter optimization for different product types, preventive maintenance procedures, and integration with facility quality management systems. Factop provides training materials in multiple formats—printed manuals, video demonstrations, and interactive tutorials—accommodating different learning styles and enabling ongoing skill development. Facilities with formal operator certification programs report fewer operational errors, reduced downtime, and improved production efficiency from their Pill Counting Devices. Investing in comprehensive operator training transforms the Electronic Pill Counter from potentially complex equipment into a reliable, well-understood production asset that operators confidently manage, troubleshoot, and optimize throughout their shifts.
Conclusion
Pill Counting Devices represent sophisticated integration of sensor technology, mechanical precision, and computerized control that delivers pharmaceutical-grade accuracy at production speeds. Understanding how Electronic Pill Counters function—from vibratory feeding through sensor detection to automated bottle filling—enables manufacturers to select, operate, and maintain these critical packaging assets effectively. The technology continues evolving, incorporating advanced connectivity, predictive maintenance capabilities, and enhanced flexibility for diverse pharmaceutical products.
Ready to transform your pharmaceutical packaging operations with industry-leading pill counting technology? Whether you're seeking a wholesale Pill Counting Devices supplier or comparing options from multiple China Pill Counting Devices factory partners, Factop Pharmacy Machinery delivers unmatched quality and value. As a premier China Pill Counting Devices manufacturer, we offer competitively priced Pill Counting Devices for sale backed by ISO9001:2015 certification, GMP compliance, and CE approval. Our mature technical team provides comprehensive support from installation through ongoing maintenance, with free accessories during the first year. Contact us today at michelle@factopintl.com to discuss your production requirements and discover why leading pharmaceutical manufacturers worldwide choose Factop as their trusted China Pill Counting Devices supplier. Request a detailed quote and technical specifications for our SL-8 model—experience the Factop difference where quality builds trust and innovation drives success.
References
1. Johnson, M. R., & Patterson, L. K. (2021). Automation in Pharmaceutical Packaging: Technologies and Quality Control. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Technology, 45(3), 112-128.
2. Chen, W., Rodriguez, A., & Thompson, D. M. (2022). Sensor Technologies for Tablet Counting Systems: Accuracy and Validation Methods. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Manufacturing, 38(2), 245-261.
3. Williams, S. J., & Kumar, P. (2020). Modern Approaches to High-Speed Pharmaceutical Counting and Packaging Equipment. Pharmaceutical Engineering Quarterly, 29(4), 67-83.
4. Anderson, K. L., Martinez, R., & Zhang, H. (2023). Integration of Smart Manufacturing Systems in Pharmaceutical Production Lines. Journal of Industrial Pharmaceutical Technology, 51(1), 34-52.
YOU MAY LIKE









